- Published on
Building AI Agent Workflows with Python & TypeScript
- Authors

- Name
- Wahyu Ikbal
- @wahyuikbal
Akhir-akhir ini, AI agent lagi booming, sedang naik daun di kalangan developer dan engineer. Buat kamu yang belum tahu, AI Agen adalah implementasi dari proses LLM, di mana LLM dilengkapi tools, memory, dan kemampuan untuk mengambil keputusan. Anggap saja sebagai assistent yang bisa mengerjakan tugas, ndak hanya sekedar memberi output berupa teks.
Konsep AI agent ini sangat powerful, terutama ketika beberapa agent berkolaborasi dalam sebuah sistem. Proses interaksi dan koordinasi antar-agent ini disebut workflows. Nah, dalam artikel ini, kita tidak akan fokus pada teori AI agent secara mendalam, melainkan lebih ke sisi engineering dan praktiknya. Jadi, pastikan kamu sudah memiliki pemahaman dasar terkait RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) dan LLM sebelum melanjutkan.
Building an Effective Agent Workflow
Di bagian ini, kita akan belajar pola-pola umum yang sering digunakan dalam sistem agentic yang sudah diterapkan di berbagai aplikasi. Nah, kali ini kita akan mempraktikkannya menggunakan Vercel AI SDK dan Langgraph. Sebagai tambahan, saya akan menjelaskan sedikit tentang LangGraph dan AI SDK. Jika kamu sudah familiar dengan framework ini, kamu bisa langsung melompat ke bagian implementasi kode.
Why LangGraph?
LangGraph adalah library yg dibangun di atas LangChain, didesain untuk aplikasi berbasis LLM, Make Langgraph jadi sat set buat sistem agent yang kompleks karena kemampuannya mengelola task-task rumit menjadi terstruktur. Keunggulan utamanya ada pada validasi data menggunakan Pydantic dan workflow yang jelas untuk menangani alur kerja, sehingga membuatnya mudah dikembangkan.
Why Vercel AI SDK
Vercel AI SDK adalah Typescript library yang dirancang untuk pengembangan aplikasi dan berbasis artificial intelligence. TypeScript library for building AI applications. Library ini sangat cocok dalam pengembangan aplikasi react framework seperti React, Next.js, Svelte, dan Vue.
AI SDK Core memiliki berbagai function yang dirancang untuk text generation, structured data generation, dan tool usage. Fungsi-fungsi ini menggunakan pendekatan standar untuk setup prompt dan settings, sehingga memudahkan penggunaan berbagai, diantaranya:
- streamText: Stream text and tool calls. Kamu bisa make function ini di beberapa kasus seperti chat bots dan content streaming.
- streamObject: Stream a structured object that matches a Zod schema. Function untuk generate UIs berbasis object, kurang lebih seperti json.
Vercel ai sdk juga menyediakan AI SDK UI yang mempermudah pembuatan interface berbasis LLM. Oleh karena itu, ini adalah library favorit saya ketika mengembangkan aplikasi ai di next js.
Workflow Patterns
Workflow atau alur kerja adalah sistem yang mengatur langkah-langkah untuk menyelesaikan tugas atau mencapai tujuan.
Konsep workflow sering kita jumpai di kehidupan sehari-hari. Contohnya di perkuliahan dan kita mengikuti suatu organisasi yang terstruktur, atau di lingkungan pekerjaan dimana terdapat sistem.
Kalau kamu ingin penjelasan lebih detail, kamu bisa baca research dari Anthropic di sini. Research dari Anthropic ini jadi referensi wajib buat banyak developer ai, dan bisa jadi bahan belajar tambahan buatmu juga. Di antaranya oke jadi urutannya gimana dulu nih
- Prompt Chaining (Sequential Processing)
- Routing
- Parallelization
- Orchestrator-Worker
- Evaluator-optimizer
Untuk kode yang ingin Anda pelajari, Anda dapat cek di github atau memeriksa reponya di akhir artikel ini.
Set up workflow
Sebelum memulai pertama kali kita set up terlebih dahulu framework yang kita gunakan. Kamu bisa pilih salah satu mau yang Typescript atau yang Python. API yang kita pakai disini make groq provider. Jangan lupa install library nya terlebih dahulu
Setting up Typescript with Vercel AI SDK
require('dotenv').config();
import { generateObject } from 'ai'; // generate json output
import { z } from 'zod'; // schema declaration
import { createGroq } from '@ai-sdk/groq'; // provider
const groq = createGroq({
baseURL: 'https://api.groq.com/openai/v1',
apiKey: process.env.GROQ_API_KEY || "",
});
Set up Python with langgraph
import os
from langchain_groq import ChatGroq
# Load environment variables
load_dotenv()
# Initialize Groq client
groq = ChatGroq(
api_key=os.getenv("GROQ_API_KEY"),
base_url="https://api.groq.com/openai/v1"
)
Prompt Chaining
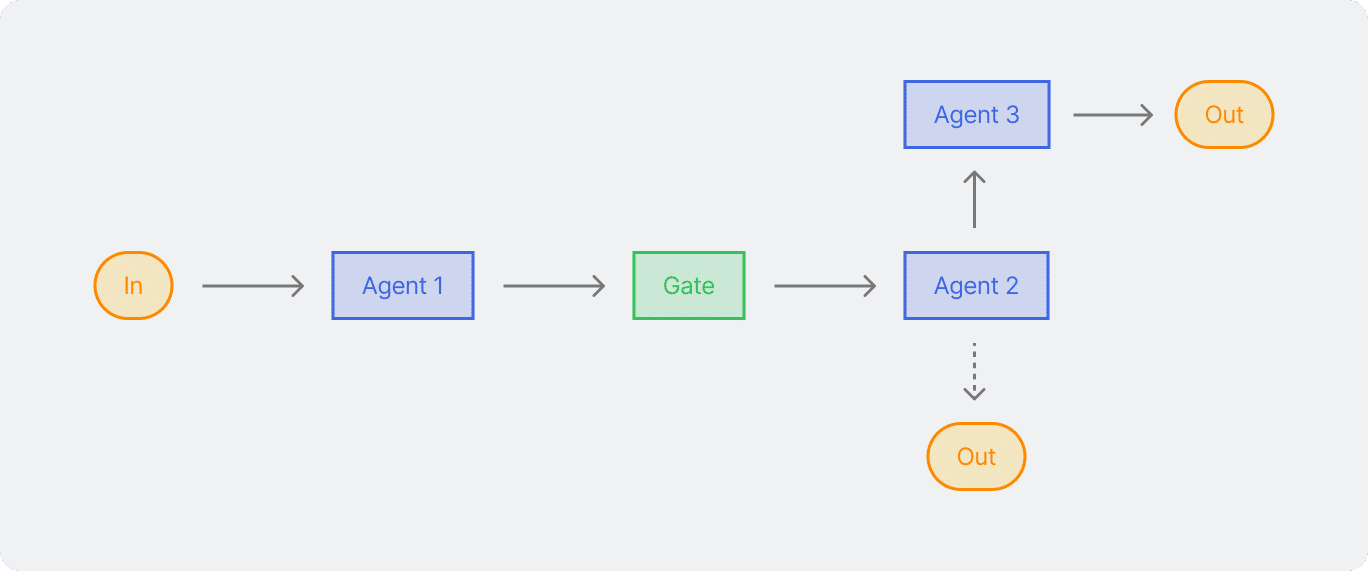
Ini adalah workflow yang paling sederhana, Prompt chaining itu memecah satu task menjadi beberapa langkah, dengan melibatkan beberapa output dari satu prompt sebagai input untuk yang berikutnya. Pola ini ideal untuk task yang urutanya jelas langkah tiap langkah
Contohnya, ketika bikin copywriting untuk sebuah brand. Dimulai dari agent A yang merangkai CTA, agent B menilai aspek emosional, agent C menilai kesesuaian dengan tone brand, dan seterusnya. Setiap proses berjalan secara urut, hasil output dari satu langkah jadi input untuk langkah selanjutnya.
async function implementFeature(featureRequest: string) {
// Orchestrator: Plan the implementation
const { object: implementationPlan } = await generateObject({
model: groq('llama-3.3-70b-versatile'),
schema: z.object({
files: z.array(
z.object({
purpose: z.string(),
filePath: z.string(),
changeType: z.enum(['create', 'modify', 'delete']),
}),
),
estimatedComplexity: z.enum(['low', 'medium', 'high']),
}),
system:
'You are a senior software architect planning feature implementations.',
prompt: `Analyze this feature request and create an implementation plan:
${featureRequest}`,
});
Setelah membuat plan sebagai agent yang bertindak sebagai senior software architect, menganalisis input dan dan menghasilkan output sesuai schema. Selanjutnya
// Workers: Execute the planned changes
const fileChanges = await Promise.all(
implementationPlan.files.map(async (file) => {
// Each worker is specialized for the type of change
const workerSystemPrompt = {
create:
'You are an expert at implementing new files following best practices and project patterns.',
modify:
'You are an expert at modifying existing code while maintaining consistency and avoiding regressions.',
delete:
'You are an expert at safely removing code while ensuring no breaking changes.',
}[file.changeType];
const { object: change } = await generateObject({
model: groq('llama-3.3-70b-versatile'),
schema: z.object({
explanation: z.string(),
code: z.string(),
}),
system: workerSystemPrompt,
prompt: `Implement the changes for ${file.filePath} to support:
${file.purpose}
Consider the overall feature context:
${featureRequest}`,
});
return {
file,
implementation: change,
};
}),
);
Workflow with LangGraph python
# Define our state schema for tracking the workflow progress
class MarketingState(TypedDict):
input: str
initial_copy: str
quality_metrics: Optional[dict]
final_copy: str
messages: list[BaseMessage]
# Define quality metrics schema
class QualityMetrics(BaseModel):
hasCallToAction: bool
emotionalAppeal: int
clarity: int
def generate_initial_copy(state: MarketingState) -> MarketingState:
"""
Generates the initial marketing copy based on the input.
"""
response = groq.chat.completions.create(
model="llama-3.3-70b-versatile",
messages=[{
"role": "user",
"content": f"Write persuasive marketing copy for: {state['input']}. Focus on benefits and emotional appeal."
}]
)
state["initial_copy"] = response.choices[0].message.content
state["final_copy"] = state["initial_copy"] # Initialize final copy
return state
def evaluate_copy(state: MarketingState) -> MarketingState:
"""
Evaluates the marketing copy against quality metrics.
"""
response = groq.chat.completions.create(
model="llama-3.3-70b-versatile",
messages=[{
"role": "user",
"content": f"""Evaluate this marketing copy for:
1. Presence of call to action (true/false)
2. Emotional appeal (1-10)
3. Clarity (1-10)
Copy to evaluate: {state['final_copy']}"""
}]
)
# Parse the metrics from the response
metrics = QualityMetrics(
hasCallToAction=True, # You would parse these values from the actual response
emotionalAppeal=8,
clarity=8
)
state["quality_metrics"] = metrics.dict()
return state
def improve_copy(state: MarketingState) -> MarketingState:
"""
Improves the marketing copy if it doesn't meet quality standards.
"""
metrics = state["quality_metrics"]
# Check if improvements are needed
if (not metrics["hasCallToAction"] or
metrics["emotionalAppeal"] < 7 or
metrics["clarity"] < 7):
improvement_prompt = f"""Rewrite this marketing copy with:
{'' if metrics["hasCallToAction"] else '- A clear call to action'}
{'' if metrics["emotionalAppeal"] >= 7 else '- Stronger emotional appeal'}
{'' if metrics["clarity"] >= 7 else '- Improved clarity and directness'}
Original copy: {state['final_copy']}"""
response = groq.chat.completions.create(
model="llama-3.3-70b-versatile",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": improvement_prompt}]
)
state["final_copy"] = response.choices[0].message.content
return state
def create_marketing_workflow() -> Graph:
"""
Creates the marketing copy generation and improvement workflow.
"""
workflow = StateGraph(MarketingState)
# Add nodes
workflow.add_node("generate", generate_initial_copy)
workflow.add_node("evaluate", evaluate_copy)
workflow.add_node("improve", improve_copy)
# Add edges
workflow.add_edge("generate", "evaluate")
workflow.add_edge("evaluate", "improve")
# Set entry and exit points
workflow.set_entry_point("generate")
workflow.set_finish_point("improve")
return workflow.compile()
def generate_marketing_copy(input_text: str) -> dict:
"""
Main function to handle the marketing copy generation process.
"""
workflow = create_marketing_workflow()
result = workflow.invoke({
"input": input_text,
"initial_copy": "",
"quality_metrics": None,
"final_copy": "",
"messages": []
})
return {
"initial_copy": result["initial_copy"],
"final_copy": result["final_copy"],
"quality_metrics": result["quality_metrics"]
}
Routing
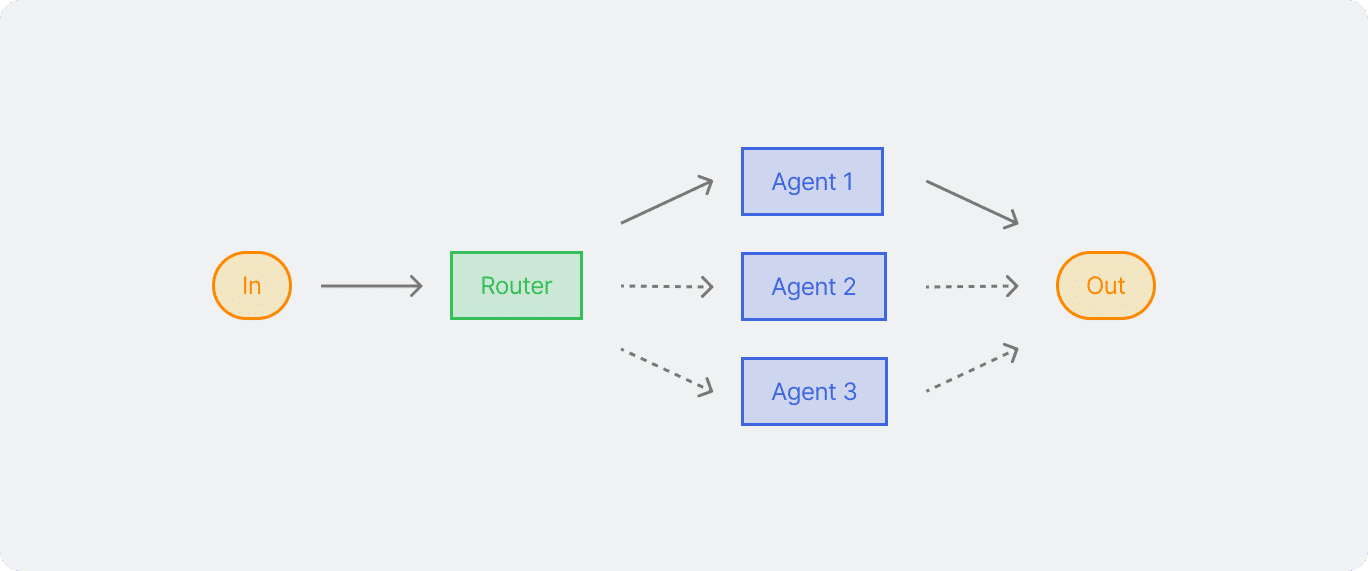
Pola ini memungkinkan model untuk menentukan jalur proses yang tepat berdasarkan konteks dan hasil sebelumnya. Pola routing bekerja dengan baik ketika ada beberapa kategori berbeda yang memerlukan penanganan khusus. Pola ini memastikan setiap kasus diproses dengan pendekatan yang paling sesuai. Seperti pada contoh di atas ini, hasil dari LLM pertama akan menentukan jalur mana yang akan diambil untuk langkah selanjutnya, menyesuaikan proses berdasarkan karakteristik input.
Pertama kita buat terlebih dahulu, routing agent nya yang mengklasifikasikan input dengan membaginya berasarkan jenis input, serta kompleksitas dan alasan detailnya.
async function handleCustomerQuery(query: string) {
const model = groq('llama-3.3-70b-versatile');
// Step 1: Classify the query type
const { object: classification } = await generateObject({
model,
schema: z.object({
reasoning: z.string(),
type: z.enum(['general', 'refund', 'technical']),
complexity: z.enum(['simple', 'complex']),
}),
prompt: `Classify this customer query:
${query}
Determine:
1. Query type (general, refund, or technical)
2. Complexity (simple or complex)
3. Brief reasoning for classification`,
});
Hasil dari klasifikasi tersebut kemudian diarahkan ke beberapa agen. Sederhana, namun pola ini bekerja dengan baik as customer service, yang tiap diarahkan ke tools seperti penjadwalan, menghubungi orang lain, dan lainnya, sehingga output yang dikeluarkan bersifat personal sesuai dengan kebutuhan pengguna.
// Route based on classification
// Determine the model and system prompt based on query type and complexity
const { text: response } = await generateText({
model:
classification.complexity === 'simple'
? groq('llama3-8b-8192')
: groq('llama-3.1-8b-instant'),
system: {
general:
'You are an expert customer service agent handling general inquiries.',
refund:
'You are a customer service agent specializing in refund requests. Follow company policies and gather necessary information.',
technical:
'You are a technical support specialist with in-depth knowledge of the product. Focus on clear, step-by-step troubleshooting.',
}[classification.type],
prompt: query,
});
Workflow with LangGraph python
# Define our state schema
class AgentState(TypedDict):
query: str
classification: dict
response: str
messages: list[BaseMessage]
# Define classification schema
class QueryClassification(BaseModel):
reasoning: str
type: Literal["general", "refund", "technical"]
complexity: Literal["simple", "complex"]
# Step 1: Classify the customer query
def classify_query(state: AgentState) -> AgentState:
"""Classifies the incoming customer query by type and complexity."""
prompt = f"""Classify this customer query:
{state['query']}
Determine:
1. Query type (general, refund, or technical)
2. Complexity (simple or complex)
3. Brief reasoning for classification"""
response = groq.chat.completions.create(
model="llama-3.3-70b-versatile",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]
)
# Parse the classification from the response
classification = QueryClassification(
reasoning=response.choices[0].message.content,
type="technical", # You would parse this from the response
complexity="simple" # You would parse this from the response
)
state["classification"] = classification.dict()
return state
# Step 2: Generate response based on classification
def generate_response(state: AgentState) -> AgentState:
"""Generates a response based on the query classification."""
# Select model based on complexity
model = "llama3-8b-8192" if state["classification"]["complexity"] == "simple" else "llama-3.1-8b-instant"
# Select system prompt based on query type
system_prompts = {
"general": "You are an expert customer service agent handling general inquiries.",
"refund": "You are a customer service agent specializing in refund requests. Follow company policies and gather necessary information.",
"technical": "You are a technical support specialist with in-depth knowledge of the product. Focus on clear, step-by-step troubleshooting."
}
response = groq.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompts[state["classification"]["type"]]},
{"role": "user", "content": state["query"]}
]
)
state["response"] = response.choices[0].message.content
return state
# Create the workflow graph
def create_customer_service_workflow() -> Graph:
"""Creates the customer service workflow graph."""
# Initialize the graph
workflow = StateGraph(AgentState)
# Add nodes
workflow.add_node("classify", classify_query)
workflow.add_node("respond", generate_response)
# Add edges
workflow.add_edge("classify", "respond")
# Set entry and exit points
workflow.set_entry_point("classify")
workflow.set_finish_point("respond")
return workflow.compile()
# Main execution function
def handle_customer_query(query: str) -> dict:
"""Handles a customer query through the workflow."""
# Initialize workflow
workflow = create_customer_service_workflow()
# Execute workflow
result = workflow.invoke({
"query": query,
"classification": {},
"response": "",
"messages": []
})
return {
"classification": result["classification"],
"response": result["response"]
}
Parallelization
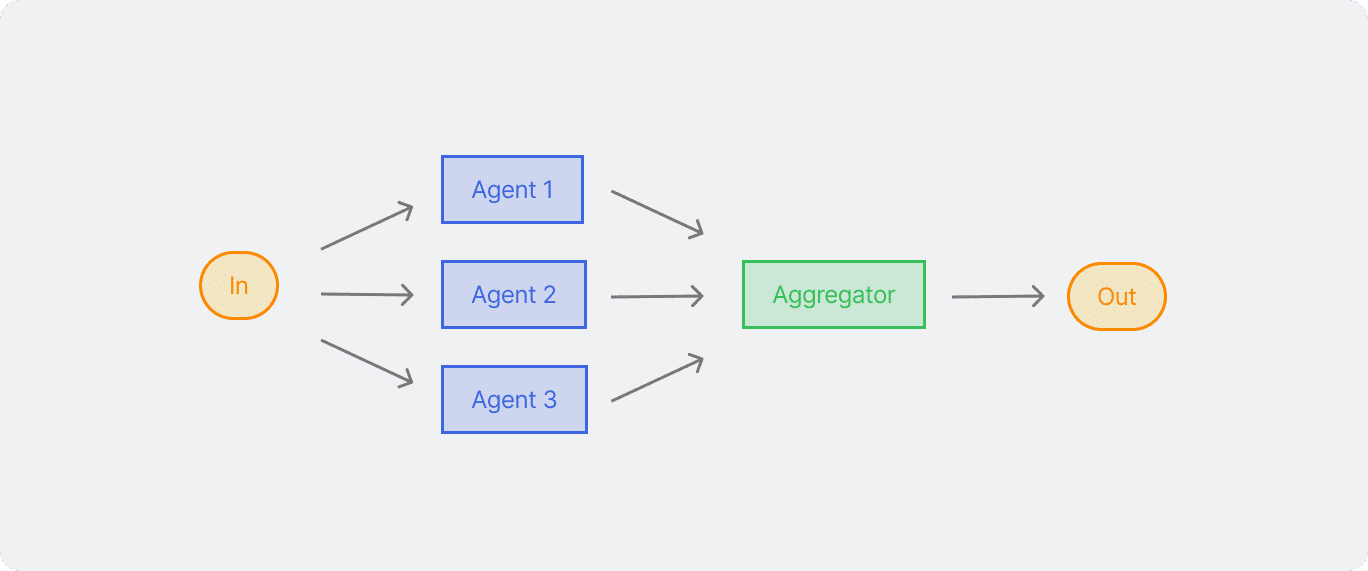
LLMs terkadang perlu untuk berjalan secara bersamaan dan menggabungkan outputnya untuk hasil yang lebih akurat. Workflow ini cukup efektif ketika task yang panjang dapat dipecah menjadi beberapa bagian lalu berjalan bersamaan supaya berjalan lebih cepat. Untuk task yang kompleks dan perlu banyak pertimbangan, LLMs biasanya menghasilkan lebih baik daripada lebih fokus ke specific attention dari suatu konteks.
Dalam workflow parallelization ini, terbagi menjadi 2 variasi, diantaranya:
- Sectioning: Memecah task menjadi beberapa subtask yang berjalan bersamaan
- Voting: Menjalankan beberapa kali task yang sama untuk menghasilkan output yang berbeda
Seperti cara kerja sebuah tim IT yang berfokus di pengembangan aplikasi, ada yang fokus di bagian performa, quality, dan security. Jadi untuk alur prompt generate websitenya dipecah di beberapa bagian aspek supaya hasil yang didapatkan ndak hanya bekerja tapi juga memiliki performa yang stabil dan punya sisi keamanan yang tinggi.
Pertama kita perlu bikin spesialist yang bekerja secara bersamaan dengan pesan yang kurang lebih sama.
// Run parallel reviews
const [securityReview, performanceReview, maintainabilityReview] =
await Promise.all([
generateObject({
model, system:
'You are an expert in code security. Focus on identifying security vulnerabilities, injection risks, and authentication issues.',
schema: z.object({
vulnerabilities: z.array(z.string()),
riskLevel: z.enum(['low', 'medium', 'high']),
suggestions: z.array(z.string()),
}), prompt: `Review this code: ${code}`,
}),
generateObject({
model, system:
'You are an expert in code performance. Focus on identifying performance bottlenecks, memory leaks, and optimization opportunities.',
schema: z.object({
issues: z.array(z.string()),
impact: z.enum(['low', 'medium', 'high']),
optimizations: z.array(z.string()),
}), prompt: `Review this code: ${code}`,
}),
generateObject({
model, system:
'You are an expert in code quality. Focus on code structure, readability, and adherence to best practices.',
schema: z.object({
concerns: z.array(z.string()),
qualityScore: z.number().min(1).max(10),
recommendations: z.array(z.string()),
}), prompt: `Review this code: ${code}`,
}),
]);
Selanjutnya kita perlu menggabungkan semua object nya jadi satu. Kita butuh satu agent sebagai Aggregator. Yang perlu review dan meringkas, bila perlu tambahkan juga task koreksi untuk meminimalisir kesalahan.
// Aggregate results using another model instance
const { text: summary } = await generateText({
model, system: 'You are a technical lead summarizing multiple code reviews.',
prompt: `Synthesize these code review results into a concise summary with key actions:
${JSON.stringify(reviews, null, 2)}`,
});
Workflow with LangGraph python
# Define response schemas using Pydantic
class SecurityReview(BaseModel):
vulnerabilities: List[str] = Field(default=[])
risk_level: str = Field(default="low")
suggestions: List[str] = Field(default=[])
class PerformanceReview(BaseModel):
issues: List[str] = Field(default=[])
impact: str = Field(default="low")
optimizations: List[str] = Field(default=[])
class MaintainabilityReview(BaseModel):
concerns: List[str] = Field(default=[])
quality_score: int = Field(default=10)
recommendations: List[str] = Field(default=[])
# Define a function to perform a review
def review_code(model, system_prompt: str, code: str, response_schema):
"""
Conducts a specialized review based on the provided system prompt and schema.
"""
messages = [
SystemMessage(content=system_prompt),
HumanMessage(content=f"Review this code:\n{code}")
]
response = model.invoke(messages)
return response_schema.parse_raw(response.content)
# Define the workflow graph
class ReviewState(BaseModel):
code: str
security: SecurityReview = None
performance: PerformanceReview = None
maintainability: MaintainabilityReview = None
summary: str = ""
graph = StateGraph(ReviewState)
def security_review_node(state: ReviewState):
model = create_groq_model()
state.security = review_code(model, "You are an expert in code security...", state.code, SecurityReview)
return state
def performance_review_node(state: ReviewState):
model = create_groq_model()
state.performance = review_code(model, "You are an expert in code performance...", state.code, PerformanceReview)
return state
def maintainability_review_node(state: ReviewState):
model = create_groq_model()
state.maintainability = review_code(model, "You are an expert in code quality...", state.code, MaintainabilityReview)
return state
def summarize_reviews(state: ReviewState):
model = create_groq_model()
messages = [
SystemMessage(content="You are a technical lead summarizing multiple code reviews."),
HumanMessage(content=f"Synthesize these code review results:\n{json.dumps(state.dict(), indent=2)}")
]
response = model.invoke(messages)
state.summary = response.content
return state
# Add nodes to the graph
graph.add_node("security_review", security_review_node)
graph.add_node("performance_review", performance_review_node)
graph.add_node("maintainability_review", maintainability_review_node)
graph.add_node("summary", summarize_reviews)
# Define parallel execution
graph.add_edge("security_review", "summary")
graph.add_edge("performance_review", "summary")
graph.add_edge("maintainability_review", "summary")
graph.set_entry_point(["security_review", "performance_review", "maintainability_review"])
graph.set_finish_node("summary")
workflow = graph.compile()
Orchestrator-Workers

Di orchestrator workers workflow, LLM yang pertama (orchestrator) membedah task dan mendelegasikan ke caranya mirip seperti decomposition dan meringkas hasilnya menjadi satu. Di LLM yang pertama ini berperan penting dalam mengkooridnasi dan mengeksekusi spesialisasi workers. Tiap worker optimal untuk subtask yang spesifik.
Mari berpikir seperti sebuah tim. Pada contoh kali ini . Di tim kali ini ada beberapa bagian ya ada di bagian Business Analyst, Content Strategist, Social Media Manager, Marketing Analyst. Kemudian dari instruksi project manager, dilakukan sebuah pengukuran tingkat kesulitan, jenis penugasan dan delegasi tugas.
async function implementTask(taskRequest: string) {
const { object: taskPlan } = await generateObject({
model: groq('llama-3.3-70b-versatile'),
schema: z.object({
tasks: z.array(
z.object({
purpose: z.string(),
taskName: z.string(),
changeType: z.enum(['create', 'modify', 'delete']),
})
),
estimatedEffort: z.enum(['low', 'medium', 'high']),
}),
system: 'You are a Project Manager responsible for designing an efficient task execution strategy.',
prompt: `Create a work plan for the following task:
${taskRequest}`,
});
const taskChanges = await Promise.all(
taskPlan.tasks.map(async (task) => {
// Determine job roles based on task type
const workerSystemPrompt = {
create: {
'Audience research': 'You are a Business Analyst. You are responsible for conducting in-depth research on the target audience.',
'Content creation': 'You are a Content Strategist. You design engaging content strategies tailored to the audience.',
'Account management': 'You are a Social Media Manager. You manage and optimize social media accounts.',
'Performance analysis': 'You are a Marketing Analyst. You analyze data and measure the success of marketing strategies.',
}[task.taskName] || 'You are an expert professional in this field.',
modify: {
'Account management': 'You are a Social Media Manager. You improve account management strategies to be more effective.',
}[task.taskName] || 'You are a specialist enhancing task efficiency.',
delete: 'You are an Operations Manager. You identify unnecessary tasks and remove them efficiently.',
}[task.changeType];
Setelah Product manager berhasil mendelegasikan tugas, selanjutnya kita gunakan apa yang ada di pola parallel sebelumnya dan mendelegasikan ke karyawan
const { object: change } = await generateObject({
model: groq('llama-3.3-70b-versatile'),
schema: z.object({
explanation: z.string(),
actionItems: z.array(z.string()),
}),
system: workerSystemPrompt,
prompt: `Implement changes for the following task:
- ${task.taskName}
Purpose of change: ${task.purpose}
Explain the reason for the change and provide a list of necessary action items.`,
});
Workflow with LangGraph python
class Task(BaseModel):
purpose: str
task_name: str
change_type: Literal["create", "modify", "delete"]
class TaskPlan(BaseModel):
tasks: List[Task]
estimated_effort: Literal["low", "medium", "high"]
def generate_task_plan(task_request: str) -> TaskPlan:
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="llama-3.3-70b-versatile",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a Project Manager responsible for designing an efficient task execution strategy."},
{"role": "user", "content": f"Create a work plan for the following task: {task_request}"}
],
response_format="json"
)
return TaskPlan(**response["choices"][0]["message"]["content"])
def implement_task_change(task: Task):
worker_prompts = {
"create": {
"Audience research": "You are a Business Analyst responsible for audience research.",
"Content creation": "You are a Content Strategist designing content strategies.",
"Account management": "You are a Social Media Manager optimizing accounts.",
"Performance analysis": "You are a Marketing Analyst measuring strategy success."
},
"modify": {
"Account management": "You are a Social Media Manager improving strategies."
},
"delete": "You are an Operations Manager identifying unnecessary tasks."
}
system_prompt = worker_prompts.get(task.change_type, {}).get(task.task_name, "You are an expert in this field.")
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="llama-3.3-70b-versatile",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": f"Implement changes for the task: {task.task_name}\nPurpose: {task.purpose}\nExplain why and list action items."}
],
response_format="json"
)
return response["choices"][0]["message"]["content"]
Evaluation/Feedback Loops
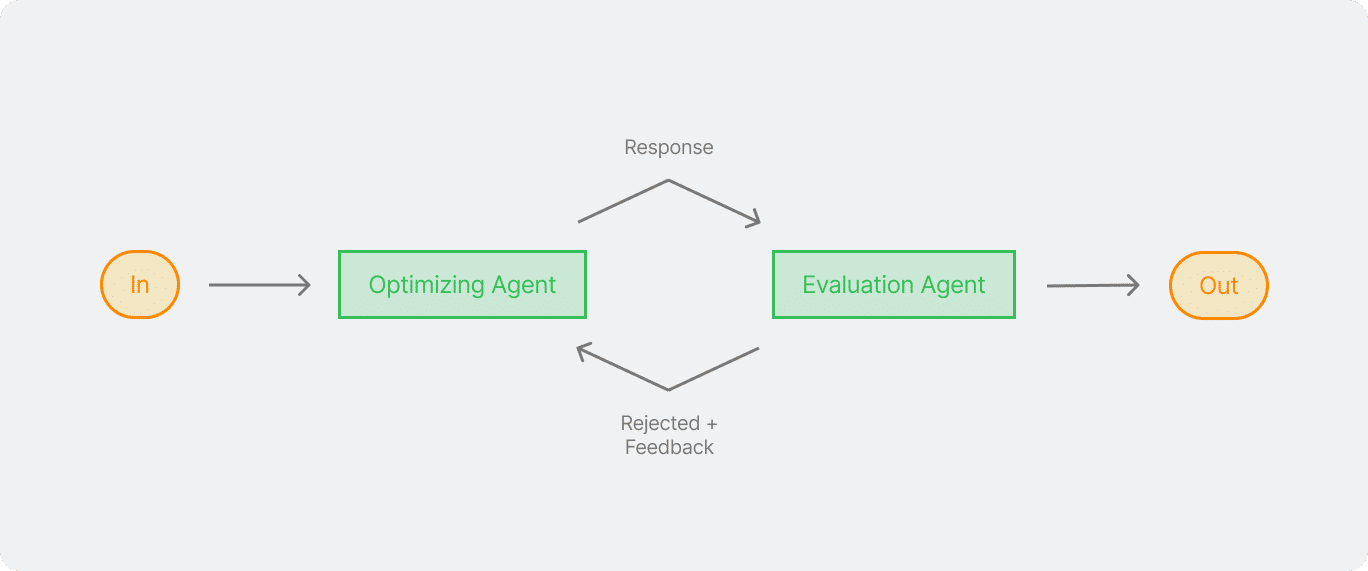
Nyuruh chatgpt buat bikin skripsi itu bukan hal yang mudah ya. Kasian chatgpt mikir sendirian. Jadi perlu adanya feedback dari agent tambahan untuk memperbaiki kualitas hasil output dengan terus mengiterasi seiring bertambahnya bagian bagian ya, seperti latar belakang, isi, kesimpulan. Untuk itu perlu adanya evaluator disini untuk memberikan feedback dan respon dari output yang ia terima
// Initial article generation
const { text: article } = await generateText({
model: groq('llama-3.1-8b-instant'),
system: 'You are a writer. Your task is to write a concise article in only 6 sentences! You might get additional feedback from your supervisor!',
prompt: `Write a 6-sentence article on the topic: ${topic}`,
});
while (iterations < MAX_ITERATIONS) {
// Evaluate current article
const { object: evaluation } = await generateObject({
model: groq('llama-3.3-70b-versatile'), // use a larger model to evaluate
schema: z.object({
qualityScore: z.number().min(1).max(10),
clearAndConcise: z.boolean(),
engaging: z.boolean(),
informative: z.boolean(),
specificIssues: z.array(z.string()),
improvementSuggestions: z.array(z.string()),
}),
system: "You are a writing supervisor! Your agency specializes in concise articles! Your task is to evaluate the given article and provide feedback for improvements! Repeat until the article meets your requirements!",
prompt: `Evaluate this article:
Article: ${currentArticle}
Consider:
1. Overall quality
2. Clarity and conciseness
3. Engagement level
4. Informative value`,
});
if (
evaluation.qualityScore >= 8 &&
evaluation.clearAndConcise &&
evaluation.engaging &&
evaluation.informative
) {
break;
}
// Generate improved article based on feedback
const { text: improvedArticle } = await generateText({
model: groq('llama-3.3-70b-versatile'), // use a larger model
system: 'You are an expert article writer.',
prompt: `Improve this article based on the following feedback:
${evaluation.specificIssues.join('\n')}
${evaluation.improvementSuggestions.join('\n')}
Current Article: ${currentArticle}`,
});
currentArticle = improvedArticle;
iterations++;
}
return {
finalArticle: currentArticle,
iterationsRequired: iterations,
};
}
Workflow with Langgraph python
# Node 1: Generate initial article
def generate_initial_article(input_data: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
model = "llama-3.1-8b-instant"
system = "You are a writer. Your task is to write a concise article in only 6 sentences! You might get additional feedback from your supervisor!"
prompt = TextPrompt(f"Write a 6-sentence article on the topic: {input_data['topic']}")
generate_text_node = GenerateTextNode(model=model, system=system, prompt=prompt)
result = generate_text_node.execute()
return {"current_article": result.text, "iterations": 0}
node1 = Node(name="generate_initial_article", function=generate_initial_article)
# Node 2: Evaluate article quality
def evaluate_article_quality(input_data: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
model = "llama-3.3-70b-versatile"
schema = ObjectSchema({
"qualityScore": (int, 1, 10),
"clearAndConcise": bool,
"engaging": bool,
"informative": bool,
"specificIssues": List[str],
"improvementSuggestions": List[str]
})
system = "You are a writing supervisor! Your agency specializes in concise articles! Your task is to evaluate the given article and provide feedback for improvements! Repeat until the article meets your requirements!"
prompt = TextPrompt(f"Evaluate this article:\n\nArticle: {input_data['current_article']}\n\nConsider:\n1. Overall quality\n2. Clarity and conciseness\n3. Engagement level\n4. Informative value")
generate_object_node = GenerateObjectNode(model=model, schema=schema, system=system, prompt=prompt)
result = generate_object_node.execute()
return {"evaluation": result.object}
node2 = Node(name="evaluate_article_quality", function=evaluate_article_quality)
# Node 3: Check if quality meets threshold
def check_quality_threshold(input_data: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
evaluation = input_data["evaluation"]
if (evaluation["qualityScore"] >= 8 and
evaluation["clearAndConcise"] and
evaluation["engaging"] and
evaluation["informative"]):
return {"meets_threshold": True}
else:
return {"meets_threshold": False}
node3 = Node(name="check_quality_threshold", function=check_quality_threshold)
# Node 4: Generate improved article based on feedback
def improve_article(input_data: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
model = "llama-3.3-70b-versatile"
evaluation = input_data["evaluation"]
system = "You are an expert article writer."
prompt = TextPrompt(f"Improve this article based on the following feedback:\n{evaluation['specificIssues']}\n{evaluation['improvementSuggestions']}\n\nCurrent Article: {input_data['current_article']}")
generate_text_node = GenerateTextNode(model=model, system=system, prompt=prompt)
result = generate_text_node.execute()
return {"current_article": result.text, "iterations": input_data["iterations"] + 1}
node4 = Node(name="improve_article", function=improve_article)
# Node 5: Final output
def final_output(input_data: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
print(f"Final Article:\n{input_data['current_article']}")
print(f"Iterations Required: {input_data['iterations']}")
return {}
node5 = Node(name="final_output", function=final_output)
# Define edges between nodes
edge1 = Edge(source=node1, target=node2)
edge2 = Edge(source=node2, target=node3)
edge3 = Edge(source=node3, target=node4, condition=lambda x: not x["meets_threshold"])
edge4 = Edge(source=node3, target=node5, condition=lambda x: x["meets_threshold"])
edge5 = Edge(source=node4, target=node2)
# Add nodes and edges to the graph
graph.add_node(node1)
graph.add_node(node2)
graph.add_node(node3)
graph.add_node(node4)
graph.add_node(node5)
graph.add_edge(edge1)
graph.add_edge(edge2)
graph.add_edge(edge3)
graph.add_edge(edge4)
graph.add_edge(edge5)
Workflow with LangGraph python
class Task(BaseModel):
purpose: str
task_name: str
change_type: Literal["create", "modify", "delete"]
class TaskPlan(BaseModel):
tasks: List[Task]
estimated_effort: Literal["low", "medium", "high"]
def generate_task_plan(task_request: str) -> TaskPlan:
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="llama-3.3-70b-versatile",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a Project Manager responsible for designing an efficient task execution strategy."},
{"role": "user", "content": f"Create a work plan for the following task: {task_request}"}
],
response_format="json"
)
return TaskPlan(**response["choices"][0]["message"]["content"])
def implement_task_change(task: Task):
worker_prompts = {
"create": {
"Audience research": "You are a Business Analyst responsible for audience research.",
"Content creation": "You are a Content Strategist designing content strategies.",
"Account management": "You are a Social Media Manager optimizing accounts.",
"Performance analysis": "You are a Marketing Analyst measuring strategy success."
},
"modify": {
"Account management": "You are a Social Media Manager improving strategies."
},
"delete": "You are an Operations Manager identifying unnecessary tasks."
}
system_prompt = worker_prompts.get(task.change_type, {}).get(task.task_name, "You are an expert in this field.")
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="llama-3.3-70b-versatile",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": f"Implement changes for the task: {task.task_name}\nPurpose: {task.purpose}\nExplain why and list action items."}
],
response_format="json"
)
return response["choices"][0]["message"]["content"]
Kapan menggunakan Typescript dan Python
Vercel AI SDK dan langgraph adalah salah satu framework yang cukup lengkap dan dokumentasi yang rapi. Selain Vercel AI SDK juga ada rekomendasi framework lainnya seperti
Agentic, AI agent standard library that works with any LLM and TS AI SDK.
Agno, open-source python framework for building agentic systems
Rivet, a drag and drop GUI LLM workflow builder; and
Crew ai, Python Framework for orchestrating collaborative AI agents
Dengan menggunakan framework membuat kita bisa dengan mudah menggunakan pola standard seperti tools, memory, component dan menghubungkanya dengan memanggil parameter tertentu.
While Python has traditionally been the dominant language in AI and ML development due to its extensive libraries and frameworks, TypeScript — a superset of JavaScript — has emerged as a strong contender for building scalable, maintainable, and efficient AI/ML applications.
Menggunakan Typescript dan Python tergantung kebutuhan, jika butuh cepat untuk pengembangan fullstack aplikasi typescript cukup tanpa menambah stack lagi, jika ingin terpisah dan membangun agent yang lebih kompleks. Python lebih direkomendasikan untuk membangun AI agent karena dukungan library AI/ML yang lengkap dan lebih banyaknya framework, sedangkan TypeScript cocok jika fokus pada integrasi dengan react framework utamanya pada fullstack developer
Baik Python ataupun Typescript, hingga framework lain bisa cek source codenya disini
https://github.com/wahyudesu/multiple-ways-to-build-ai-agents